In the world of industrial plastics, choosing the right material can define the success and longevity of your project. Among the most widely used materials, Polycarbonate and Polyethylene stand out for their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Yet, while both are popular in global markets, their performance, appearance, and technical characteristics differ significantly. For companies, manufacturers, and bulk buyers, understanding the key differences between these two polymers is essential for making informed investment decisions. In this article, we present a detailed comparison of Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene, focusing on their industrial applications, structural properties, and long-term value in construction, agriculture, and manufacturing sectors.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Polyethylene and What Is It Made Of?

Polyethylene (PE) is one of the most widely used types of plastic in the world. Known for its light weight, high flexibility, and excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, it plays a vital role in industries such as packaging, construction, and manufacturing.
Polyethylene is composed of ethylene molecules (C₂H₄) — hydrocarbon compounds typically derived from natural gas or crude oil. It is produced through a process called polymerization, in which small ethylene monomers are chemically bonded to form long polymer chains.
The type and performance of polyethylene vary depending on its density and production method. The main types include:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Rigid, strong, and impact-resistant — commonly used in pipes, tanks, and containers.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): More flexible and transparent — used in plastic bags, films, and packaging.
- LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene): Combines durability with flexibility — ideal for industrial wrapping and agricultural films.
Thanks to its chemical inertness, moisture resistance, and lightweight nature, polyethylene remains a practical and cost-effective choice across multiple industrial and commercial applications — making it a key material in the ongoing debate of Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene.
What Is Polycarbonate and What Is It Made Of?
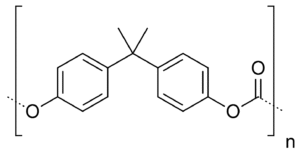
Polycarbonate (PC) is a high-performance engineering plastic known for its exceptional strength, clarity, and versatility. It serves as an advanced alternative to glass and metal in many industrial and architectural applications, including construction, roofing systems, machinery, lighting, and electronic products.
Chemically, polycarbonate consists of polymers containing carbonate groups (–O–(C=O)–O–) within their molecular chains. It is typically produced through the reaction of Bisphenol A (BPA) with Phosgene, or via newer, safer manufacturing methods adopted in modern production.
This unique molecular structure gives polycarbonate an outstanding combination of rigidity, transparency, heat resistance, and impact strength, making it one of the most reliable materials in engineering and a key contender in the Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene comparison.
Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene: Key Material Properties
Below is a professional comparison of the key properties of Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene, from an industrial and large-scale project perspective:
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Strength & Impact Resistance | Much stronger than glass and most plastics; highly resistant to breakage and cracking. | Good impact resistance but lower than polycarbonate; can deform under pressure. |
| Transparency & Light Transmission | Excellent clarity (85–90%), comparable to glass. | Mostly opaque or semi-transparent depending on the grade. |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures up to 120°C without deformation. | Lower heat tolerance, up to around 80°C. |
| Weight | Very lightweight compared to glass. | Slightly lighter than polycarbonate. |
| UV Resistance | Comes with a UV-protective layer for outdoor durability. | Poor UV resistance unless UV stabilizers are added. |
| Service Life | Over 15 years with consistent performance. | Shorter lifespan, especially under direct sunlight. |
| Flexibility & Formability | Can be easily cut, bent, and thermoformed without cracking. | More flexible but less dimensionally stable and rigid. |
| Thermal & Acoustic Insulation | Excellent, especially for twin-wall polycarbonate sheets. | Good, but less effective in retaining heat. |
| Sustainability & Recycling | Fully recyclable and eco-friendly; long-term durability. | Recyclable but less durable over time. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance and longevity. | More economical for basic or temporary applications. |
In summary, polycarbonate is the preferred choice for applications requiring strength, clarity, and long service life, such as roofing, skylights, and facades. Meanwhile, polyethylene remains a practical solution for packaging, piping, and low-cost temporary uses.
Applications of Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene
The applications of Polycarbonate (PC) and Polyethylene (PE) differ significantly based on the nature of industrial projects and material requirements. Both are versatile plastics, but each excels in specific sectors due to its unique performance characteristics.
Applications of Polycarbonate (PC)
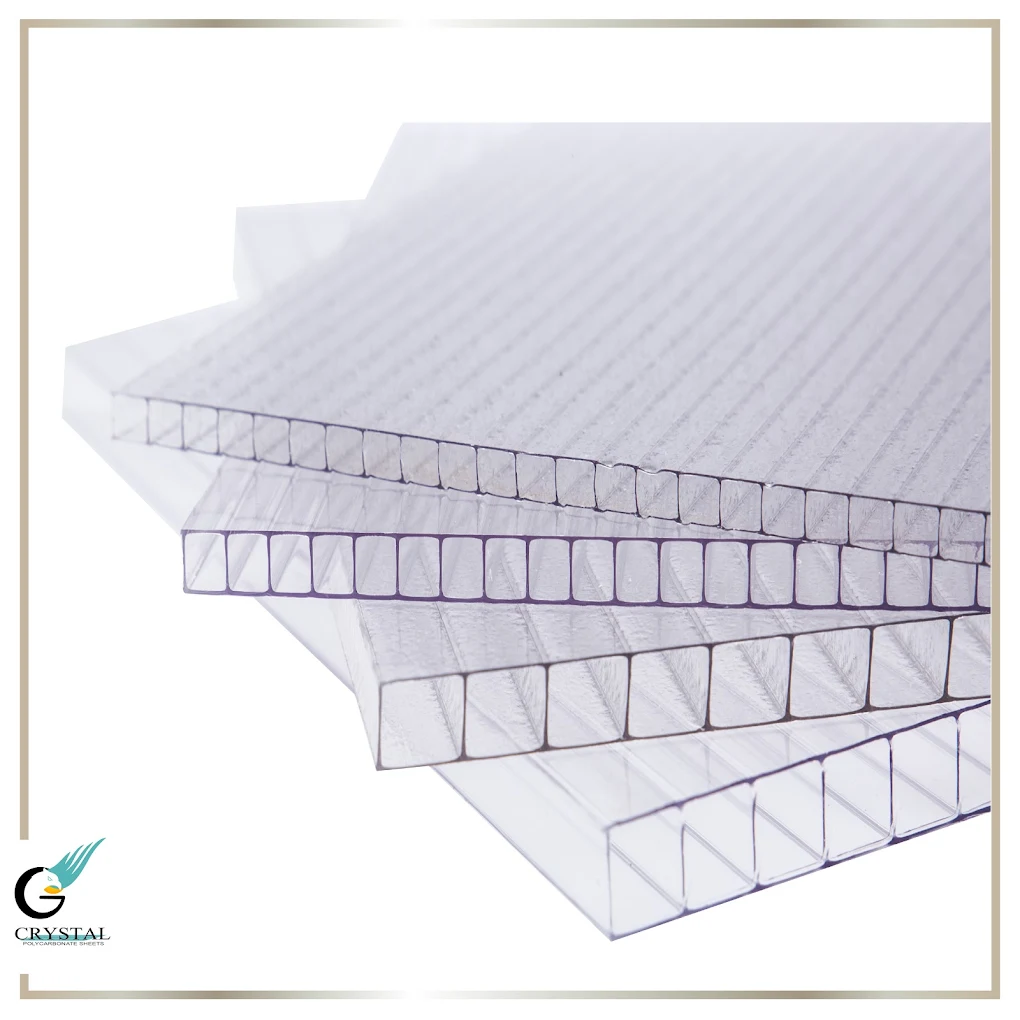

- Architectural Structures: Used in roofing systems, canopies, skylights, transparent facades, and wind barriers.
- Agricultural Projects: Ideal for greenhouses, tunnel covers, and agricultural windows thanks to its excellent thermal insulation.
- Industrial Sectors: Serves as protective machine guards, transparent safety barriers, and equipment covers.
- Lighting & Energy: Used in manufacturing lenses, light diffusers, and solar panel covers.
- Security & Protection: Applied in bulletproof glass, safety shields, and security partitions.
- Design & Advertising: Suitable for interior partitions, signage, and modern architectural decorations.
Applications of Polyethylene (PE)
- Infrastructure: Used in water and drainage pipes, as well as plastic insulation materials.
- Agriculture: Commonly used for greenhouse films, flexible irrigation tunnels, and agricultural packaging.
- Packaging & Industry: Widely used for industrial bags, stretch films, and chemical containers.
- Electrical & Energy: Acts as insulation for wires, cables, and protective electrical covers.
- Household Products: Found in lightweight furniture, storage containers, and everyday low-cost items.
Polycarbonate is the preferred choice for advanced, long-term applications that require high strength, transparency, and thermal insulation.
Polyethylene, on the other hand, is ideal for cost-effective, temporary uses where flexibility and lightweight properties are more important than rigidity.
With over 20 years of manufacturing excellence, G-Crystal Plastic Industries stands as a global leader in producing and supplying premium polycarbonate sheets for wholesalers and large-scale projects. The company manufactures under European quality standards, offering products with performance guaranteed to last over 15 years.
Industries That Use Both Polycarbonate and Polyethylene
Both Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene are widely used across various industries that require lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easily moldable materials. Despite their differences in strength, transparency, and lifespan, they often complement each other in key industrial applications. Below are the main sectors where both materials are used, along with practical examples:
Agricultural Industry
Both materials are used in agricultural coverings and tunnel systems. Polycarbonate is preferred for long-lasting greenhouse panels, while Polyethylene is commonly used for temporary agricultural films, mulch covers, and irrigation bags.
Packaging and Manufacturing
Both are used in producing films, containers, and bottles. Polyethylene is ideal for lightweight products like food packaging and plastic bags, whereas Polycarbonate is chosen for durable containers, transparent protective covers, and impact-resistant packaging.
Infrastructure and Construction
Polycarbonate is widely used in roofing sheets, skylights, and transparent facades, offering high strength and visual appeal. In contrast, Polyethylene is used in pipes, insulation materials, and waterproofing layers, thanks to its flexibility and resistance to moisture.
Industrial and Engineering Applications
Polycarbonate serves as protective guards and transparent safety shields for machinery, while Polyethylene is utilized in tanks, mechanical components, and chemical-resistant panels.
Consumer and Everyday Products
Polycarbonate is used in safety goggles, lighting covers, and electronic casings, whereas Polyethylene is found in plastic furniture, kitchenware, and storage containers.
In short, both Polycarbonate and Polyethylene play vital roles across agricultural, industrial, and consumer markets — but the final choice depends on whether the priority is transparency and strength (Polycarbonate) or flexibility and cost-efficiency (Polyethylene).
Advantages of Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene in Construction Projects
In the construction sector, choosing the right material is essential to balance durability, aesthetics, and cost.
Polycarbonate outperforms Polyethylene in projects requiring resistance to weathering and visual appeal. Its sheets are widely used for canopies, skylights, domes, and facades, providing over 85% light transmission and excellent UV protection.
Polycarbonate also offers superior thermal and sound insulation, with a service life exceeding 15 years, making it a sustainable and long-term solution for large-scale residential and commercial developments.
Polyethylene, on the other hand, is suitable for temporary insulation layers and low-cost roofing covers, but it cannot match the stability or aesthetic quality of Polycarbonate in high-performance architectural applications.
Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene in Agriculture and Industry
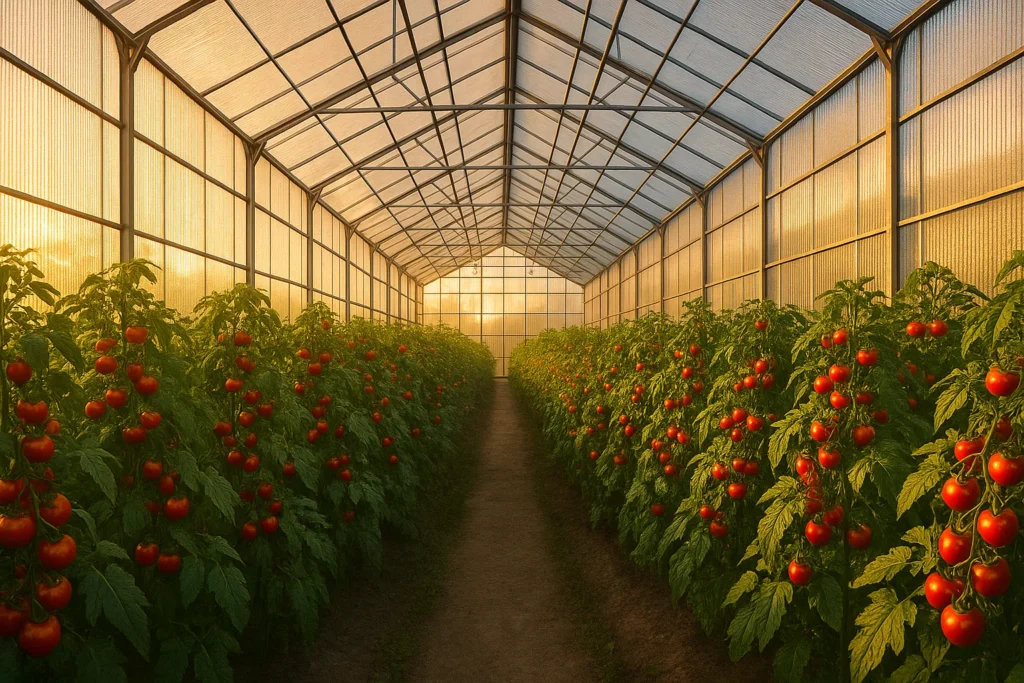

In both the agricultural and industrial sectors, the choice between Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene depends on the project’s lifespan and application needs.
In agriculture, Polycarbonate is the ideal material for greenhouse and tunnel coverings, offering strong thermal insulation and UV protection for long-term installations. In contrast, Polyethylene is commonly used for flexible temporary agricultural films, mulch covers, and irrigation bags, where short-term use and low cost are the priorities.
In industrial applications, Polycarbonate excels in demanding environments, serving as protective machine covers, transparent safety shields, and impact-resistant barriers in production lines. Meanwhile, Polyethylene is favored for industrial tanks, pipes, and insulation materials, thanks to its excellent chemical resistance and lightweight flexibility.
In summary, Polycarbonate delivers professional, long-term performance, while Polyethylene offers a cost-effective, short-term solution for projects that prioritize economy over longevity.
How to Choose the Right Material for Your Project
When deciding between Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene, consider these practical factors to ensure you select the most suitable material for your application:
- Environmental Conditions: For outdoor or high-temperature environments, choose Polycarbonate. For indoor or short-term setups, Polyethylene is sufficient.
- Durability & Lifespan: If you need a material that lasts over 15 years, opt for Polycarbonate. For temporary or low-cost projects, Polyethylene is more economical.
- Light & Aesthetics: Use Polycarbonate for projects requiring high light transmission and an elegant visual appearance.
- Insulation: For superior thermal and sound insulation, select twin-wall Polycarbonate sheets.
- Budget: If cost efficiency is the top priority, Polyethylene offers the best value.
G-Crystal Plastic Industries provides a wide range of Polycarbonate sheet solutions tailored for industrial and architectural projects worldwide, supported by expert technical consultation to help you choose the ideal product for your specific application.
The Best Plastic Sheet Manufacturer in Egypt and the Middle East

G-Crystal Plastic Industries stands as one of the leading plastic sheet manufacturers in Egypt, the Middle East, and worldwide. With over 20 years of expertise in the industry, G-Crystal specializes in the production and global export of polycarbonate sheets of all types to more than 60 countries. Combining advanced manufacturing technology with premium raw materials, the company delivers high-performance plastic sheets designed to meet the needs of large corporations, factories, and wholesale distributors across industrial, architectural, and agricultural sectors.
G-Crystal’s product range includes:
- Solid Polycarbonate Sheets
- Twin Wall Polycarbonate Sheets
- Embossed Polycarbonate Sheets
- Diva Crystal Pattern Sheets
- Crystal Pattern Sheets
All G-Crystal products are engineered for superior thermal and sound insulation, UV protection, and long-term durability exceeding 15 years. Each product is certified according to European quality standards and carries three ISO certifications, ensuring consistent excellence for large-scale projects and international buyers.
The company also provides flexible global shipping solutions including FOB, CIF, CFR, EXW, and DDP, supported by a professional logistics network that guarantees fast delivery and safe handling from factory to destination.
Whether you are an importer, distributor, or industrial or construction project owner, partnering with G-Crystal Plastic Industries means gaining access to guaranteed quality, competitive prices, and professional global support.
Request a Quote Now and let G-Crystal connect your business to success — anywhere in the world.
Frequently Asked Questions: Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene
1. What is the main difference between polycarbonate and polyethylene?
Polycarbonate is stronger, more transparent, and resistant to high temperatures and UV rays, while polyethylene is lighter and cheaper but less durable and suitable for short-term applications.
2. Which material is better for roofing and canopies?
Polycarbonate sheets are the better choice for roofing and canopies thanks to their UV resistance, excellent thermal insulation, and long lifespan of over 15 years.
3. Can polyethylene be used in greenhouses?
Yes, polyethylene is often used in temporary greenhouse covers and tunnels, but it does not last as long as polycarbonate sheets, which offer better insulation and plant protection.
4. Which one is more impact-resistant?
Polycarbonate has around 200 times the impact resistance of glass and is significantly stronger than polyethylene.
5. Which material withstands high temperatures better?
Polycarbonate can resist heat up to 120°C without deformation, while polyethylene softens at around 80°C.
6. Which option is more economical?
Polyethylene offers a lower initial cost, but polycarbonate is a long-term investment due to its high durability and extended service life.
7. Are both materials recyclable?
Yes, both polycarbonate and polyethylene are recyclable, but polycarbonate retains its quality longer after recycling.
Whether your project requires a long-lasting transparent material or a cost-efficient short-term solution, the Polycarbonate vs Polyethylene comparison clearly shows that G-Crystal Plastic Industries delivers the ideal solution — with world-class quality and specifications tailored to every industrial or architectural application.


