Polycarbonate (PC) is one of the most advanced engineering thermoplastics, transforming industries worldwide thanks to its unique balance of strength, lightness, and transparency. More than just a practical alternative to glass and metals, polycarbonate has become a versatile solution in construction, architecture, medical devices, electronics, and the automotive sector.
Renowned for its exceptional impact resistance, ability to withstand high temperatures, and UV protection, polycarbonate is the preferred choice for companies and manufacturers seeking long-lasting, safe, and sustainable materials. In today’s global market—where efficiency, safety, and eco-friendliness are top priorities—polycarbonate stands out as the material that delivers on all fronts.
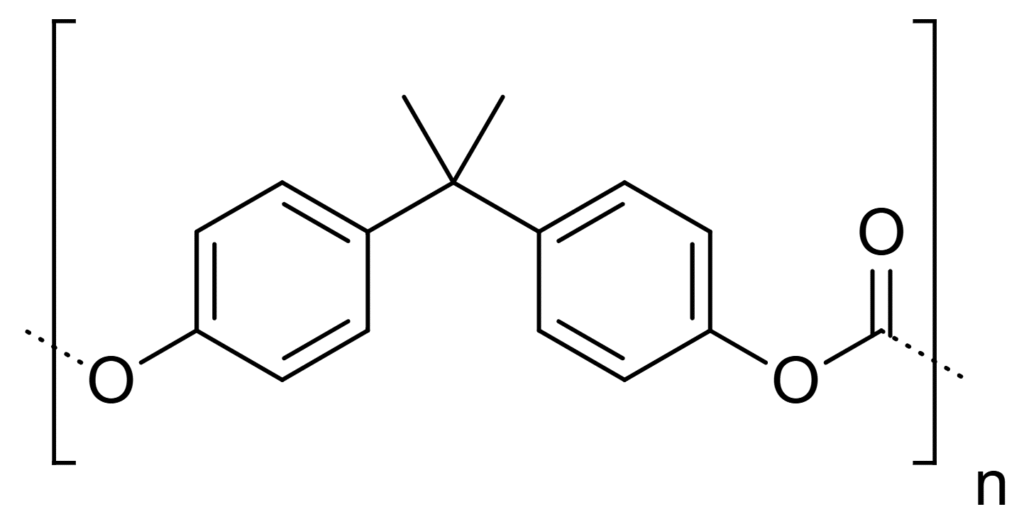
What Are Polymers?
Polymers are macromolecules composed of repeating structural units called monomers, bonded covalently to form long chains. Their ability to adapt properties such as rigidity, elasticity, transparency, and chemical resistance makes them indispensable in both everyday life and advanced industries.
They can be natural (proteins, cellulose, starch, DNA) or synthetic (polyethylene, polypropylene, nylon, polycarbonate). Synthetic polymers, in particular, are critical to the production of plastics, coatings, fibers, rubber, medical devices, and even cutting-edge applications in aerospace and biomedical engineering.
Types of Synthetic Polymers
Synthetic polymers are categorized according to their behavior under heat and elasticity:
1. Thermoplastics
- Can be reshaped with heat and recycled.
- Examples: Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polycarbonate (PC).
2. Thermosets
- Permanently hardened by heat; cannot be remolded.
- Examples: Epoxy resins, Phenolics.
3. Elastomers
- Extremely elastic; return to original form after stretching.
- Examples: Synthetic rubber, Silicone.
Polycarbonate: Best-in-Class Performance
Polycarbonate is regarded as one of the most advanced synthetic polymers, combining:
- High mechanical strength
- Glass-like transparency
- Outstanding resistance to impact, heat, and UV radiation
Modern production techniques often replace toxic phosgene with Diphenyl Carbonate (DPC), making PC safer and more environmentally friendly.
Its versatility makes it indispensable in:
- Construction: roofing sheets, skylights, façades
- Agriculture: greenhouse coverings, plant protection
- Medical and electrical industries: devices requiring durability and heat resistance
- Transportation: shatterproof windows, lightweight automotive and aviation parts
The blend of lightweight durability, safety, and long lifespan makes PC the go-to material for projects prioritizing efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Polycarbonate vs. Other Polymers
| Material | Key Properties | Advantages | Limitations | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Transparent, impact-resistant, withstands up to 120°C | High impact strength, thermal & acoustic insulation, long lifespan, UV protection | Higher cost compared to basic plastics, but significantly longer service life | Roofing, canopies, greenhouses, safety goggles, medical devices |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Lightweight, flexible, moisture-resistant | Affordable, easy to mold, chemical resistant | Poor heat & UV resistance, low mechanical strength | Plastic bags, pipes, packaging |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Stronger than PE, resists up to 100°C | Lightweight, chemical resistant, non-toxic | Brittle at low temperatures, UV degradation | Food/medical packaging, auto parts, synthetic fibers |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | Extremely transparent, lightweight | Excellent aesthetics, UV resistant | More brittle than PC, lower impact strength | Signage, décor, aquariums, windows |
| PVC | Rigid or flexible, waterproof | Affordable, good electrical insulation, durable | Environmentally unfriendly, brittle at low temperatures | Pipes, cables, flooring, plastic windows |
Key Properties of Polycarbonate
1. Chemical Properties
- High stability against most diluted acids and alkalis.
- Oxidation resistance ensures long-term durability.
- Eco-friendly when manufactured with DPC instead of phosgene.
2. Thermal Properties
- Temperature range: -40°C to 120°C without deformation.
- Thermoformable without losing mechanical strength.
- Flame retardant when additives are included.
3. Optical Properties
- High transparency: up to 88–90% light transmission.
- UV protection: prevents yellowing over time.
- Light diffusion: available in clear or patterned finishes.
4. Mechanical Properties
- Impact resistance: up to 200 times stronger than glass.
- Flexibility allows tolerance of pressure and impact without breaking.
- Rigidity and durability suitable for demanding environments.
5. Environmental & Practical Properties
- Service life: exceeds 15 years.
- Recyclable in some grades.
- Versatile applications across construction, agriculture, electronics, automotive, and safety equipment.
Practical Applications of Polycarbonate
1. Construction
- Roofing and skylights resistant to impact and temperature.
- Transparent façades with UV protection.
- Shatterproof windows for schools, hospitals, and security facilities.
2. Agriculture & Environment
- Greenhouses with superior thermal insulation for improved crop yields.
- Plant coverings resistant to humidity and UV rays.
3. Electrical & Electronics
- Enclosures and housings with impact and heat resistance.
- Control panels and components for industrial use.
4. Medical Industry
- Instruments, syringes, and high-strength medical devices.
- Safety goggles and protective equipment.
- Shatterproof automobile windows.
- Lightweight, durable components for airplanes and trains.
6. Everyday Products
- Safety glasses and watch covers.
- Food- and beverage-safe containers.
- Advertising signs and interior design panels.
High-Quality Polycarbonate Sheet Manufacturing
The production of premium-quality polycarbonate sheets requires cutting-edge technology and strict quality control:
- Raw materials: High-purity Bisphenol A (BPA) or eco-friendly DPC.
- Production technique: Extrusion ensures consistent thickness and smooth surfaces.
- UV protection layer: Prevents yellowing and maintains clarity for decades.
- Quality testing: Optical transmission, impact resistance, heat tolerance, thickness, and uniformity.
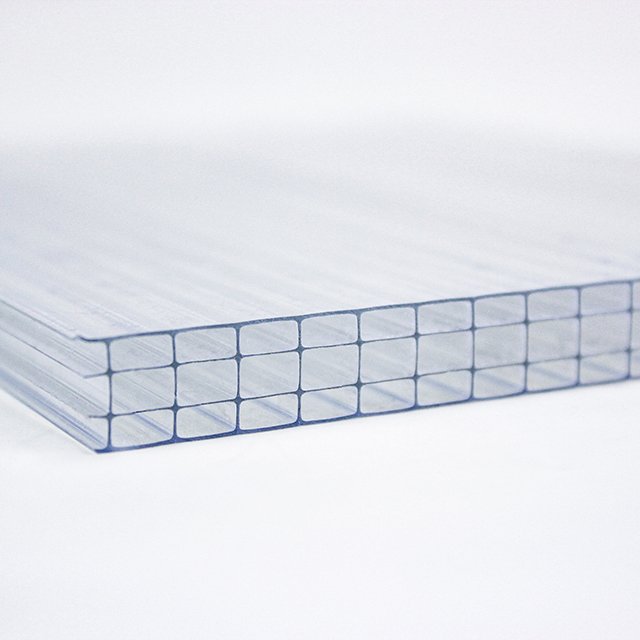
Types of Polycarbonate Sheets:
- Solid Sheets: High impact strength and clarity.
- Twin-Wall Sheets: Excellent thermal and acoustic insulation.
- Multi-Wall Sheets: Added insulation and uniform light distribution.
- Corrugated Sheets: Wavy design for enhanced structural strength.
- Textured Sheets: Decorative finishes such as crystal patterns.
G-Crystal: A Global Leader in Polycarbonate
With more than 20 years of expertise and exports to over 60 countries, G-Crystal is recognized as a worldwide leader in the production of high-quality polycarbonate sheets.
Competitive Advantages:
- Certified quality: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, and CE compliance.
- Proven experience: Decades of manufacturing and global distribution.
- Professional management: End-to-end process monitoring using advanced extrusion and UV-coating technologies.
- Product range: Solid, twin-wall, multi-wall, and corrugated sheets—all rigorously tested to ensure reliability.
By combining durability, sustainability, and innovation, G-Crystal delivers polycarbonate solutions that meet the needs of large-scale construction, agriculture, and industrial projects worldwide.
Get in Touch Today
Secure premium-quality polycarbonate sheets, certified to ISO and CE global standards, with exclusive offers for companies, distributors, and importers worldwide.
Don’t wait—contact G-Crystal today for a free consultation and tailored business solutions.